About the Client
The client is a mid-size European Pharmaceutical company intending to develop an extended-release (ER) tablet of the marketed drug using a 505 b(2) regulatory filing for the treatment of epilepsy in humans.
The Challenge
The marketed drug showed fast absorption and the current dosing regimen for adults is 50 mg as loading/initial dose followed by 25 to 100 mg BID maintenance dose. Our client wanted to develop a once-a-day dosing regimen by making ER tablets to support the patients. The Syngene team developed an ER tablet formulation and evaluated the in vitro dissolution profile. The ER tablet showed a desirable in vitro dissolution profile. To evaluate the translatability of in vitro profile to in vivo condition, the team further conducted a pharmacokinetic study in beagle dogs.
- The plasma exposure of RLD 100 mg, BID is comparable with the Test product-1 200 mg, QD. However, percent drug release was >90% within 12 hours post-dose
- The client wanted to explore a few more formulations as the results were not as per their expectations..
Parameters | RLD PO: 100 mg, BID | Test product-1 PO: 200 mg, QD | Test product-2 PO: 200 mg, QD |
|---|---|---|---|
Cmax (ng/mL) | 9820 | 8710 | 6680 |
Tmax (h) | 1 (0.5-1) | 2 (2-2) | 2 (2-4) |
AUClast (h*ng/mL) | 50800 | 56600 | 37600 |
AUC0-12 (h*ng/mL) | 28700 | 53400 | 36500 |
% of AUC0-12M | 56% | 94% | 97% |
AUC12-36
(h*ng/mL)
| 22300 | 3270 | 1080 |
(Table 1)
The Solution
The DMPK team worked on the literature and found the difference in the PK of the marketed product in humans and the dogs, where the initial studies were performed.
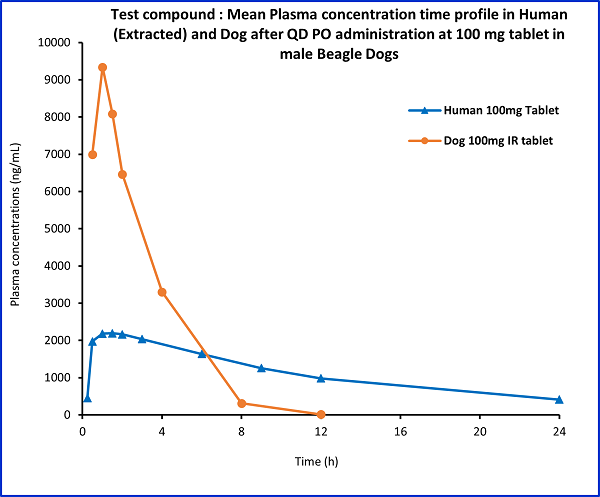
Figure (1)
- The human plasma concentration-time data of the test compound at the dose of 100 mg tablet was extracted using available online software
- The obtained plasma concentrations in humans were plotted against dog plasma concentrations at the same dose.
- The absorption profile of the test compound in dogs was different from that in humans, suggesting dogs might not be the right species for evaluating test compound extended-release formulations.
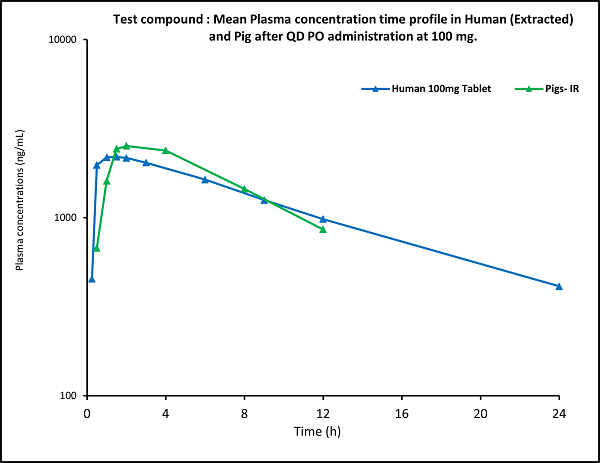
The team searched the literature and suggested that the pig could be the right species for the oral pharmacokinetic studies for oral dosage forms. The client agreed to the suggestion and proceeded with the PK study using Landrace pigs.
Figure (2)
- The plasma PK profile in pigs was comparable with that of the plasma PK profile in humans.
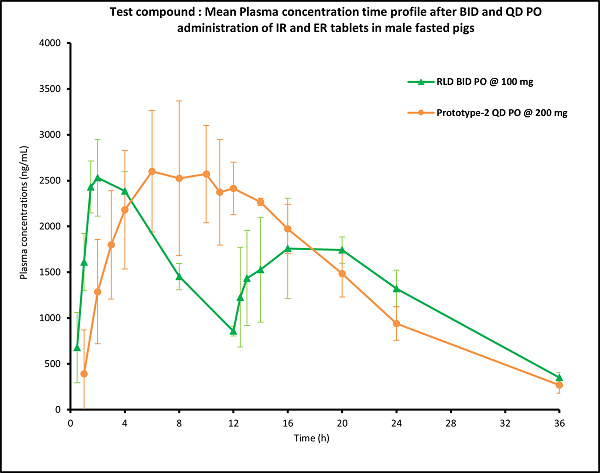
(Figure 3)
Parameters | RLD PO: 100 mg, BID | Test product-2 PO: 200 mg, QD | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Test compound | |||||||||
Cmax (ng/mL) | 2540 | 2810 | |||||||
Tmax (h) | 2 (2-4) | 10 (8-14) | |||||||
AUClast (h*ng/mL) | 47700 | 51400 | |||||||
AUC0-12 (h*ng/mL) | 19900 | 24400 | |||||||
% of AUC0-12 | 42% | 47 % | |||||||
(Table 2)
- Delayed absorption was observed in all the test prototypes compared to RLD treatment indicating delayed release of drug from the tablet dosage.
- The plasma exposure of the test compound in the First 12 hours was around 40 to 50% of the total plasma exposure, suggesting extended release of the drug from the tablet dosage forms
Conclusion
Choosing the right assay at the right time for the right compound is the essence of the success of Drug Discovery and Development.
- By choosing the right animal species (from dogs to pigs), considerable resources, money, and time were saved.
- The client was extremely happy with the results and awarded the extended projects for manufacturing tablets for clinical supplies.
- Based on the success of human clinical trials, Syngene will work on registration batches followed by commercial supplies.