Introduction
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are lab-engineered proteins that mimic the ability of the immune system to neutralize harmful pathogens. Produced by identical immune cells cloned from a single parent cell, these antibodies target a specific antigen with high precision. Their applications span across medicine, treating cancers, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases, as well as diagnostics and research. By binding to specific molecules on cells or pathogens, mAbs can block harmful processes, mark cells for destruction, or deliver targeted therapies¾—an approach that elevates precision targeting and demands robust mAb manufacturing for consistent quality. Thus, the clinical impact of mAbs now depends on scalable mAb manufacturing, from cell line development to fill-finish.
Advantages of using mAbs in treatment
Precision targeting
Monoclonal antibodies are engineered to bind with exceptional specificity to a single antigen epitope. This targeted binding enables precise modulation of disease-driving molecules, such as cell-surface receptors or circulating cytokines, minimizing off-target effects and improving safety compared to traditional drugs.
Custom monoclonal antibody development & personalized therapy
Driven by advances in immunology, molecular biology, and protein engineering, mAbs epitomize the evolution toward personalized medicine. They can be tailored to individual patients or molecular pathways, delivering highly customized therapeutic effects.
Versatility across diseases
mAbs are used in oncology, autoimmune disorders, chronic inflammatory diseases, infections, transplants, and more. They act via multiple mechanisms: blocking receptors, inducing cell death, delivering drugs or cytotoxic agents, and recruiting the immune system for targeted cell elimination.
Proven efficacy & widespread use
With hundreds of mAbs approved over the past decades, they consistently feature in treatment guidelines across cancer, inflammatory, and immunological conditions. Their efficacy in these domains has solidified their central role in therapy.
Manufacturing consistency and scalability in mAb production
Recombinant production in well-characterized cell lines (e.g. CHO, HEK) enables reproducible, scalable manufacture—a necessity for regulatory consistency and clinical deployment on a global scale.
mAb Therapeutics Market
According to The Insight partners, the mAb therapeutics market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.9%, reaching US$ 619.60 billion by 2031 from US$ 249.14 billion in 20241.
This unprecedented growth in mAb therapeutics is driven by the increased incidence of chronic diseases, breakthroughs in biotechnology, and the growth of personalized medicines. Some other factors include supportive regulatory policies, an increase in approval rates for novel mAb products, and strong acceptance in emerging economies.
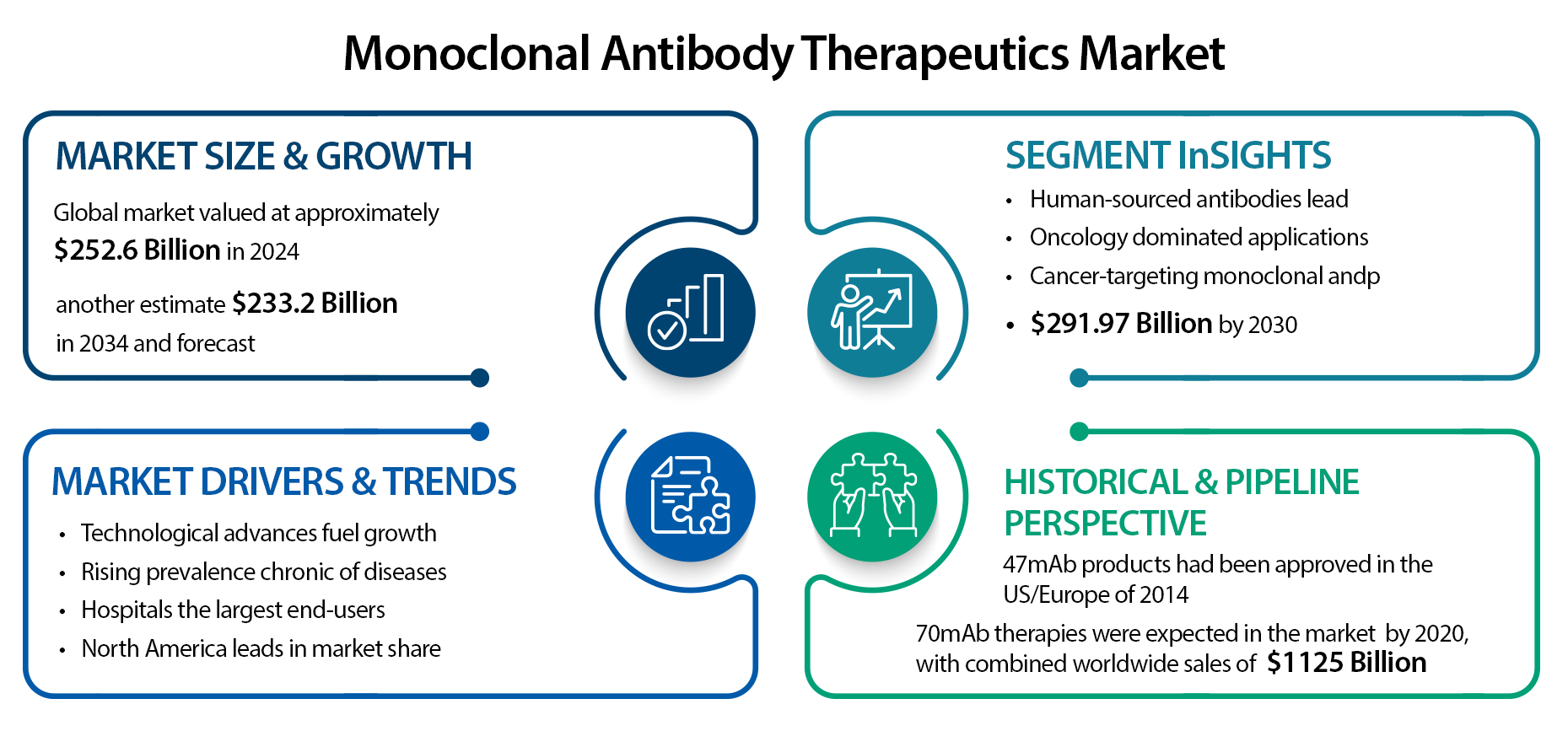
The monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapeutics market has seen impressive growth over the past few years, with projections indicating even stronger expansion ahead. According to MarketsandMarkets, the global mAb therapeutics market was valued at approximately USD 252.6 billion in 2024 and is expected to nearly double to USD 497.5 billion by 2029, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 14.5%. Similarly, BioSpace reports an estimate of USD 233.2 billion for 2024, with forecasts reaching as high as USD 919.1 billion by 2033, reflecting a CAGR of 14.7%. Broader estimates for the antibody-based therapy market—including all antibody formats—range from USD 278 billion in 2024 to nearly USD 951 billion by 2034, with annual growth rates between 11% and 13.4% (Grand View Research; Towards Healthcare; Precedence Research).
This growth is being fueled by several key trends. First, technological progress in the fields of biotechnology and protein engineering has dramatically improved the quality and function of therapeutic antibodies. Fully human and humanized monoclonal antibodies are now preferred because of their greater efficacy, lower immunogenicity, and enhanced safety profiles (Grand View Research; Beckman Coulter). In parallel, the global burden of chronic diseases continues to rise—especially cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases—leading to a sharp uptick in demand for targeted biologics like mAbs (Grand View Research; PR Newswire).
Hospitals are currently the largest end-users, accounting for an estimated 62% to 64% of mAb sales in 2025. This is due in part to the intravenous nature of many monoclonal antibody treatments, which require trained staff and clinical monitoring (Future Market Insights). However, the market is starting to shift as new delivery options—such as subcutaneous formulations—enable more outpatient and home-based care, a trend expected to grow in the coming years (PR Newswire; PharmiWeb).
In terms of geography, North America remains the dominant region, owing to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high R&D spending, and favorable regulatory environment. Still, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, driven by rising healthcare investments and expanding patient populations in countries like China and India (MarketsandMarkets; Grand View Research; Towards Healthcare).
Looking at market segmentation, monoclonal antibodies derived from human sources currently lead the market, as they offer improved safety and therapeutic outcomes. Humanized antibodies—which are mostly human with small non-human components—are also on the rise and are expected to see strong growth in the coming years (MarketsandMarkets). Among application areas, oncology dominates. Cancer-targeting mAbs alone generated USD 142.35 billion in 2024 and are projected to reach USD 291.97 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of about 12.7% (PharmiWeb; Grand View Research; BioSpace). When looking at the broader cancer mAb segment, the value stood at USD 237.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to climb to USD 494.5 billion by 2030, reflecting an annual growth of roughly 11% (Grand View Research).
From a historical standpoint, there were around 47 monoclonal antibody therapies approved in the U.S. and Europe by 2014, with steady additions of 3 to 5 new approvals per year. By 2020, it was expected that nearly 70 mAbs would be on the market, generating global sales of about USD 125 billion (PubMed; PMC). Since then, the pipeline has only expanded further, with numerous late-stage clinical trials and accelerated approvals suggesting even faster growth in the near future.
Looking ahead, monoclonal antibodies are expected to expand across autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and various forms of cancer. New categories such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and bispecific antibodies are gaining attention, offering enhanced targeting capabilities and reduced toxicity. Innovations in engineering are helping overcome resistance issues and improve treatment outcomes. While hospitals will continue to play a central role, self-administered and home-friendly formats will likely capture a growing share of the market (PR Newswire; PharmiWeb; Grand View Research).
Finally, the market is being reshaped by regulatory changes and the rise of biosimilars—cheaper alternatives to branded mAbs that offer similar safety and efficacy. Major players in the biosimilar space include Pfizer, Novartis, AbbVie, Coherus, and Biocon, all of whom are introducing new products and expanding access to mAb treatments (Grand View Research). Academic reviews from sources such as PubMed and PMC have also noted how far monoclonal antibody technology has come since its first FDA approval in 1986, with evolving standards in pharmacokinetics, dosing strategies, and clinical trial design expected to shape the next generation of therapies (PubMed; PMC).
However, the manufacturing complexity of mAbs presents significant hurdles in taking these therapies to market. This blog explores the top challenges in mAb manufacturing and Syngene’s innovative solutions for resolving them.
Challenges in Monoclonal Antibody Manufacturing
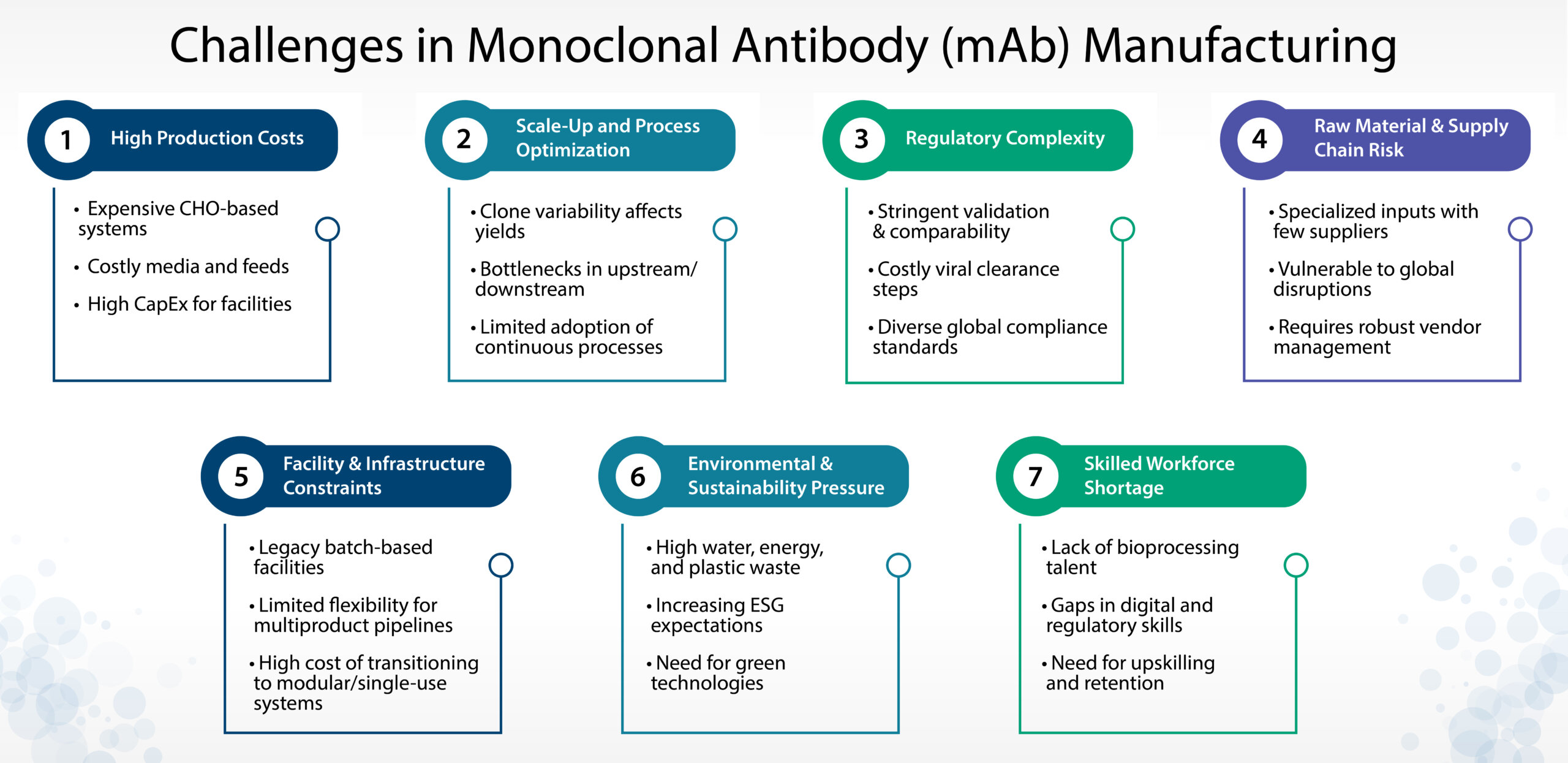
As monoclonal antibodies continue to dominate the biologics landscape, manufacturers face a host of technical, regulatory, and strategic challenges. Below are seven critical areas that influence scalability, cost-efficiency, and long-term competitiveness in mAb production.
1. High Production Costs
Monoclonal antibodies are produced in mammalian expression systems, typically Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells, which require complex bioprocessing environments. The use of high-cost media, sophisticated bioreactor systems, and extensive development timelines significantly drives up the cost of goods sold (COGS). In addition, large-scale manufacturing requires considerable capital investment in infrastructure and process equipment. Optimizing yields while maintaining quality and reducing cost remains a central concern for biologics developers.
2. Scale-Up and Process Optimization
Transitioning from laboratory-scale to commercial-scale mAb manufacturing is fraught with variability and inefficiencies. Cell line instability, clone selection challenges, and process drift can result in inconsistent yields and product quality. Upstream and downstream bottlenecks—such as low productivity clones or chromatography column limitations—can further restrict throughput. While innovations like high-density perfusion and continuous manufacturing offer promising alternatives, they are not yet industry-standard, and their adoption requires strategic investment and regulatory familiarity.
3. Regulatory Complexity
Biologics manufacturing is governed by stringent global regulations, making compliance a resource-intensive endeavor. Manufacturers must demonstrate process robustness through detailed validation, conduct impurity profiling, and carry out viral clearance studies. For biosimilars, comparability studies add another layer of complexity. Moreover, navigating divergent regulatory expectations across the US, EU, Japan, and emerging markets increases the burden on both technical and quality teams. Failure to align with evolving standards can result in delays and increased costs.
4. Supply Chain and Raw Material Constraints
The production of mAbs relies on a wide array of specialized raw materials—such as customized cell culture media, filtration membranes, and chromatography resins—often sourced from a limited number of suppliers. This dependency exposes the manufacturing process to supply chain disruptions, price volatility, and delivery delays. Events like pandemics, geopolitical tensions, or regulatory restrictions can severely impact material availability. Effective vendor risk management and strategic inventory planning are increasingly essential.
5. Facility Flexibility and Infrastructure Limitations
Traditional mAb manufacturing facilities are large, fixed-capacity, and primarily designed for single-product batch processes. As product pipelines diversify and demand becomes less predictable, the need for flexible and modular facilities is growing. Single-use technologies and ballroom concepts offer scalability and reduced cross-contamination risk, but transitioning to these models demands significant upfront investment and operational transformation. Facility design must now account for speed, adaptability, and multiproduct readiness.
6. Environmental and Sustainability Challenges
The resource-intensive nature of mAb manufacturing raises environmental concerns. High water and energy consumption, significant plastic waste from single-use systems, and emissions from HVAC operations all contribute to an unsustainable footprint. With increasing pressure from regulators and investors to implement greener practices, manufacturers are expected to adopt energy-efficient systems, closed-loop waste management, and sustainable supply chain practices. Incorporating sustainability is no longer optional—it is strategic.
7. Talent and Capability Gaps
Biologics manufacturing demands a highly specialized workforce skilled in cell culture, downstream purification, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance. However, the rapid growth of the sector has outpaced talent availability, especially in emerging geographies and fast-scaling CDMOs. The rise of digital technologies and automation further increases the need for cross-functional skills. Companies must invest in workforce development, digital training platforms, and collaborative learning ecosystems to future-proof their operations.
How Syngene’s intensified fed-batch boosts titers in mAb manufacturing
We have implemented an intensified fed-batch process for mAb manufacturing that delivers a 3-4 fold increase in production titers. This advancement addresses common challenges in mAb production, such as low yields and lengthy processes, by optimizing upstream processes and enhancing efficiency.
Our hybrid upstream strategy for mAb production encompasses both perfusion and high-seeding density methods. This approach involves:
- Modification of existing/developed fed-batch process without increasing the size of the production bioreactor
- Using a very high initial seed density (HSD) by alternating tangential flow filtration at the N-1 stage of the perfusion process.
- Using basal media (media blending strategy) with an enriched feed strategy for the N-1 stage and production
- Performing scalability with optimum aeration, agitation, and temperature shift conditions to achieve:
- Higher protein yields
- Desired protein quality
- Less accumulation of unwanted metabolites
The process is ideal for high protein production at a large scale without expanding the existing manufacturing footprint. Our unique media blending strategy keeps the culture viable for a longer time while minimizing undesired waste accumulation during the production process. With this hybrid method, customers can achieve higher titers of 7-12 g/L (3-to-4-fold increase) without impacting product quality. Further, by adopting our intensified N-1 and HSD production, the overall cost of goods (COGs) can be reduced even with fewer batches.
Discover how our intensified fed-batch process is transforming mAb production — read our complete viewpoint.
Case studies demonstrating our expertise in mAb manufacturing
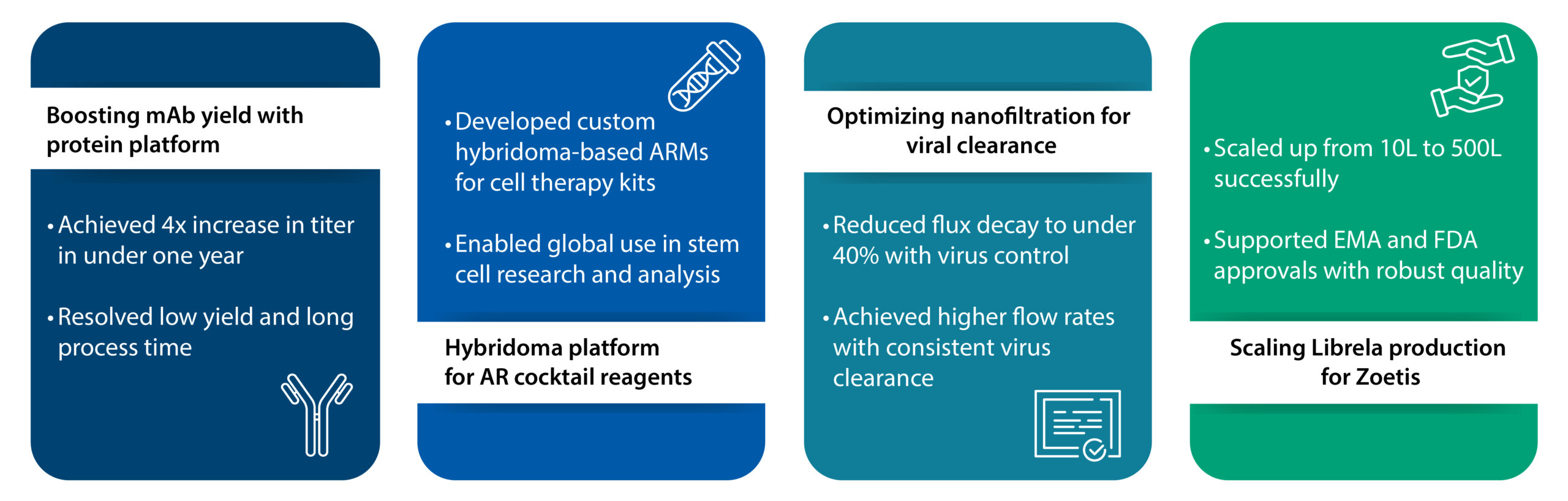
Four-fold increase in titer using our unique protein platform
A prominent biotech company focused on advancing mAb therapies for cancer treatment partnered with us to raise titers in mAb manufacturing, cutting time and COGS. We implemented our new protein platform process that resulted in a four-fold increase in titer in less than a year, significantly enhancing efficiency and reducing costs for the biopharma company. Our approach successfully addressed previous issues related to low yield and lengthy processes, enabling the production of high-quality clones ideal for mAb manufacturing. The notable increase in titer achieved within such a short timeframe underscores the effectiveness of our methodology.
To learn how we achieved a four-fold titer increase for a leading biotech company, read our case study.
Our hybridoma platform for manufacturing mAb cocktail formulations
A global biotech company partnered with us to launch new reagent kits essential in cell and gene therapy. We developed a unique hybridoma platform for them that ensured the successful integration of hybridoma cell lines with five different ancillary raw materials (ARMs). These ARMs were used to formulate three ancillary reagents (ARs), which were a cocktail of these ARMs in defined combinations and specified concentrations. The client integrated these reagents into analytical kits, providing end-users with powerful tools for stem cell identification, characterization, and analysis. The success of this project will enable researchers worldwide to accelerate their stem cell studies, supporting advancements in regenerative medicine, developmental biology, and cellular therapy.
Enhancing nanofiltration efficiency in mAb production process
Viral clearance is a critical regulatory requirement in monoclonal antibody manufacturing. However, the nanofiltration step often poses challenges due to membrane fouling and flux decay. One major pharmaceutical company was experiencing significant issues with nanofiltration during its monoclonal antibody (mAb) production process. During virus spiking at 1%- 0.5% of the load volume, they encountered reduced filtration efficiency and flux decay. Our in-house viral testing team delivered a solution that resulted in the client successfully achieving the desired target throughput with flux decay levels at under 40%. We were able to effectively control virus aggregates, resulting in a more efficient and cost-effective nanofiltration process. The optimized process enabled the client to operate at higher flow rates while maintaining effective virus clearance throughout the process.
Explore how our hybridoma platform is driving innovation in cell and gene therapy, read our case study.
Manufacturing the drug substance for Zoetis’ first-in-class mAb osteoarthritis drug
Animal health major Zoetis required a reliable manufacturing partner to support the production of Librela®, the first mAb approved for canine osteoarthritis. We enabled the right-first-time scale-up of the drug substance from 10L to 500L. For this, we met stringent process performance parameters during scale-up, including optimizing process conditions to achieve high product quality while maintaining titer consistently. Zoetis went on to receive EMA and US FDA approvals for Librela, paving the way for the commercial launch of their drug in the EU and US markets per timelines.
To find out how we optimized nanofiltration for efficient viral clearance, read our case study.
Future outlook
With around 30 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) either approved or under review in the EU and US between 2024 and 2025, the demand for reliable, scalable, and cost-effective mAb manufacturing has never been more urgent. To meet this need, biotech companies must adopt modern solutions—such as modular and flexible biomanufacturing setups, single-use technologies for faster turnaround and reduced contamination risk, automation for better process control, AI-driven tools for optimizing production, and advanced purification systems. However, implementing these improvements requires significant investment and specialized expertise.
Preferred partner
As a leading CDMO for mAb manufacturing, Syngene offers end-to-end Biologics development and manufacturing solutions for mammalian and microbial systems. Our biologics manufacturing facilities have a total installed, single-use bioreactor capacity of 50,000 Liters across the US and India. In addition, we have a sterile fill-finish facility with a total capacity of 1 million vials/day. This provides our customers with both flexibility and scale in mAb manufacturing.
Further, we employ cutting-edge automation and digitization tools at each stage of manufacturing¾ resulting in larger quantities of mAbs within a shorter timeframe. Our platform processes and expertise in process optimization also brings with it more opportunities to improve costs and reduce environmental impact¾ the latter being a growing concern with mAb production.
With over 150+ biologics projects delivered, strong regulatory track-record (FDA, PMDA,MHRA) and industry-leading titers, we are the partner of choice for biotechs seeking to accelerate their mAb programs –lab to commercial.
To know more, contact our experts
References
- https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/monoclonal-antibody-mabs-therapeutics-market-115323820.html
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/monoclonal-antibodies-market
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25529996/
- https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/antibody-therapy-market
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4622599/






