Introduction
The UN Climate Change Conference in Glasgow 2021 (COP26) highlighted the responsibility of individuals and companies in tackling the challenges of protecting our planet. With the pharmaceutical industry being a significant contributor to environmental pollution, there is an urgent need to adopt Green Chemistry at all stages of drug development – design to delivery.
Green Chemistry refers to technology, products, and processes that can minimize or eliminate the use or generation of hazardous substances during the design, development, and manufacture of chemical products. Green metric tools and technologies can positively impact the environment, people, and business growth. Further, applying a Green strategy in drug development can reduce the number of synthetic conversions, shorten the linear synthetic route, and maximize the atom economy.
In this point of view, we discuss how Syngene supports clients in developing pathbreaking therapies while ensuring minimal environmental impact in keeping with its Green Chemistry approach.
Challenges in implementing Green Chemistry
A drug’s therapeutic response depends on its molecular structure and solubility. Redesigning a drug to be readily biodegradable is like developing a new drug from scratch, as changing its structure could alter its function and efficacy. For example, processes like nitration, sulphonation, etc., require a strategy to overcome low conversion, poor selectivity, low yield, and drug delivery efficiency, not to mention the focus on addressing the large volumes of effluent. Such a change would be costly and complex, requiring subject matter experts (SMEs), high-end equipment, and instruments. Seen from a drug development perspective, this translates to two of the biggest barriers to going Green – drug efficacy and costs.
Syngene’s Green Solutions in drug development across phases
As a leading CRO/CDMO with 28 years of experience across drug discovery, development, and manufacturing (small molecules and biologics), Syngene is committed to Green Chemistry initiatives – particularly in reducing effluents and designing safer alternatives to hazardous processes. Our approach to a cost-effective route goes hand-in-hand with Green Chemistry principles1 and regulatory guidelines. We believe drug discovery and process development are the right stages for applying sustainability ideas. This would go a long way in creating a manufacturing process that has minimum environmental impact.
Our Green Chemistry approach starts at the project proposal stage with special emphasis on identifying the opportunities around safety, environmental impact, alternative, eco-friendly routes, and cost reduction. It also involves telescoping reaction steps, catalysis, possible throughputs, usage of safer solvents, and auxiliaries to ensure processes are developed with a deeper understanding, including using environmentally-benign chemical synthesis.

Tools & Processes used for Green Chemistry
Electronic Notebooks
Syngene uses electronic notebooks (ELNs) to record and share experimental data. ELNs enable the greenest possible solvent selection. They also help you calculate Green Chemistry metrics like PMI, e-factor, atom economy (minimal by-product formation), etc.
Flow Chemistry Technology
We endorse flow chemistry technology wherever possible to produce a higher quality product, reduce solvent and production costs, and increase product safety. Flow Chemistry substantially improves mixing and heat management, scalability, and energy efficiency despite some limitations. It also helps improve waste generation, safety, access to a broader range of reaction conditions, unique oppor tunities in heterogeneous catalysis, and multi-step synthesis.
Process Analytical Technology
We extensively use process analytical technology (PAT) in process R&D to develop robust and optimized processes for manufacturing. By applying PAT tools, we have significantly reduced data collection time and improved process understanding and quality while minimizing failures.
Digital Technology
We have embraced digital technology, using mathematical modeling to enable sustainable Green manufacturing. For this, we work collaboratively with chemists, process engineers, and statistical analysts. Modeling improves project performance by improving manufacturing productivity and enabling accurate planning, forecasting, and budgeting.
Syngene’s Process Modeling & Simulation Workflow to ensure a Green Process

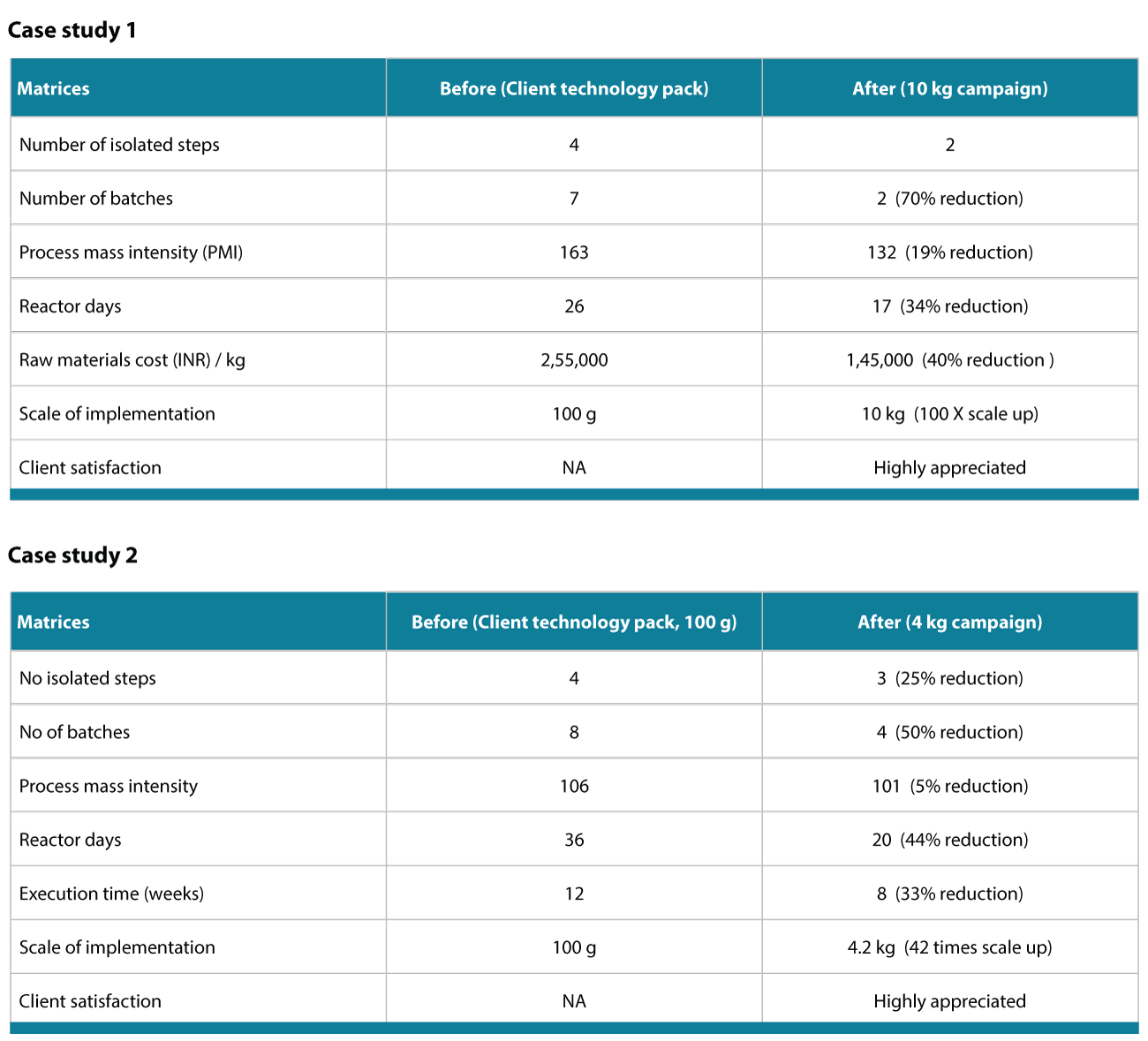
Case studies in Green Chemistry
Syngene’s action plan for continued sustainability
Syngene’s action plan for continued sustainability
Syngene is among the few CMOs/CDMOs with a roadmap that prepares us for changes in expectations, including resulting shifts in key partner selection criteria such as sustainable plants, practices, and products. Our action plan is as follows:
Develop high-standard APIs; build centralized production bases
Strictly implement international standards for environmental protection, safety, and energy conservation when working with APIs
Conduct frequent production audits and evaluations by certified authorities
Increase penetration of Green production technology
Procure less hazardous reagents, solvents, and chemicals, wherever applicable
Eliminate technologies and facilities with high VOC emissions, causing severe environmental pollution and posing a high safety risk
Overcome technical barriers and establish actions for waste reduction
Focus on the 3R principle of waste management – reduce, reuse, and recycle
Focus on treatment methodologies for waste management
Implement a plan for carbon emission reduction
Encourage departments to undertake self-assessment of CO₂ emission and establish goals accordingly
Formulate and implement a carbon-reduction emission action plan
Increase adoption of environment, occupational health, safety, and sustainability (EHSS) system
Implement an effective EHSS management system to track ESG metrics
Encourage external EHSS audits and build a Green supply chain
Conclusion
Syngene aims to limit its environmental footprint and find solutions that ensure the societal value of the company’s research is not offset by the environmental impact of the materials we use and how we use them. Where feasible, we adopt sustainable business practices and focus on interventions that increase energy efficiency and reduce waste and water footprint. As published in our Environment Social Governance Report 2020-21, we procured more than 80% of our electricity from renewable sources – a decision that is both good for the planet and our energy costs. To facilitate effective waste management and promote the recovery and reuse of materials, we have set up a state-of-the-art facility on our main site in Bengaluru for effective waste segregation and disposal, which gives us complete control of our waste management standards.
We have also been able to recycle and reuse up to 70% of the spent solvents from our operations, thereby leading to significant reductions in the generation of hazardous waste and a commensurate reduction in demand for fresh solvents. We harvest rainwater to supplement our other water sources and have an active program to reduce freshwater use across our operations. We also operate a zero-discharge approach, eliminating water pollution hazards from run-off to streams, rivers, agricultural land, and other water bodies. Our Green approach has resulted in increased customer and investor satisfaction even as we play our role in shaping a responsible future for our sector and our company.
About the authors









