Chemical Derivatization in LC-MS/MS Bioanalysis: An Overview
Chemical derivatization is a technique employed in bioanalysis to enhance ionization potential, chromatographic behaviour and stability of analytes having functional groups like aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, phenols, carboxylic acids, and amines. By employing specific derivatizing agents tailored to these functional groups, scientists can facilitate the detection and quantification of compounds at low levels in complex biological matrices, ultimately supporting accurate and reliable bioanalytical studies in drug development.
Although, chemical derivatization appears to be an easy chemical reaction, most bioanalysts face several challenges associated with the process like results reproducibility, stability of derivatization agent and derivatives, safety concerns etc. This viewpoint explores how CROs with their advanced infrastructure and extensive experience of working with clients for bioanalytical services, can bring new insights into chemical derivatization techniques – to improve detection of challenging compounds, efficiently and effectively.
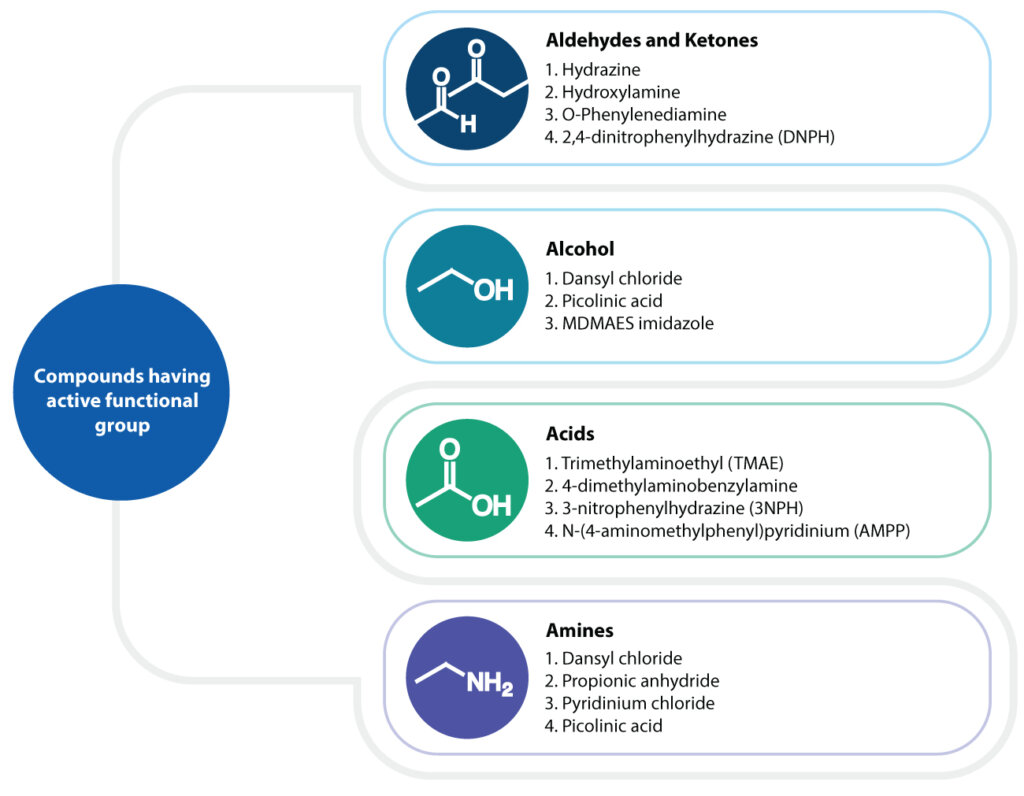
Key Challenges in Chemical Derivatization for LC-MS/MS Bioanalysis
Although, chemical derivatization appears to be an easy chemical reaction, most bio analysts have reported the following challenges associated with the process:
Optimization of conditions: The derivatization process is highly sensitive to reaction conditions. Inadequate optimization of derivatization agent concentration, temperature, pH, and reaction time, can lead to incomplete derivatization of the compound. Therefore, careful optimization of these parameters is crucial for achieving accurate and reliable results.
Results reproducibility: Attaining consistent derivatization throughout the calibration range in biological matrices is essential for quantitative determinations. Inconsistent derivatization can compromise result reproducibility and impact the detection of the lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ).
Stability of derivatization agent and derivatives: The stability of derivatizing agents must be assessed, as they can lose potency over time, necessitating fresh preparation for each reaction. Additionally, unstable derivatives may degrade, affecting the accuracy of the analysis.
Complexity in sample preparation protocol: Derivatization often requires additional sample preparation steps, increasing the complexity of the process and the potential for errors.
Safety concerns: Some derivatization reagents are hazardous (e.g., diazomethane, nitrosourea, or bromide derivatives) and require additional safety protocols for handling and disposal.
Compatibility with analytical techniques: Derivatization reactions frequently involve non-volatile inorganic or organic reagents that may deteriorate mass spectrometry operation or can degrade column performance. Examples include sodium hydroxide, diazomethane, sodium bicarbonate, and hydrazine [2]. These issues necessitate frequent maintenance of the mass spectrometer and conditioning of the chromatographic column to ensure reproducible results
Why Partner with an Experienced CRO for Chemical Derivatization
CROs with their advanced infrastructure and extensive experience of working with clients for bioanalytical services, can bring new insights into chemical derivatization techniques – to improve detection of challenging compounds, efficiently and effectively.
As a global CRO/CDMO with 30+ years of experience, we have considerable expertise in enhancing detection and sensitivity of trace compounds with chemical derivatization methods. Further, our advanced technology enables detection of compounds in their native form.
We are equipped with highly sensitive LCMS triple quad systems such as API-7500, API 6500, API-5500, API-4500 along with HRMS-API 5600 from SCIEX. For the quantification of compounds having challenges with ionization or chromatographic retention we employ chemical derivatization approaches. Here are some case studies that demonstrate our expertise in chemical derivatization aimed at accurate and precise bioanalytical results.
Case Study 1: Improving LC-MS/MS Sensitivity through Methylation-Based Chemical Derivatization
The new chemical entity (NCE) we were developing for a client was unstable, liable to non-specific binding. Direct detection was only possible at µg level. However, the expected LLOQ was 1 ng/mL in mice plasma. Conventional protein precipitation methods were not suitable to achieve this sensitivity despite the use of a high-end instrument (LC-MS/MS Sciex API 7500). Therefore, a chemical derivatization technique was adopted to alter the compound’s properties by methylating the –OH group in carboxylic acid and phosphate groups. The methylation was carried out using TMS-DM (Trimethylsilyldiazomethane) as the derivatization reagent. This procedure aimed to methylate the compound at five positions, thereby improving its detection limit and sensitivity in the analytical method and achieving the desired LLOQ of 1 ng/mL. Initially, the chemical derivatization was not efficient and resulted in reproducibility issues. These issues were addressed through stringent temperature control, continuous vortexing, and using a fresh derivatizing reagent solution at the time of the reaction.
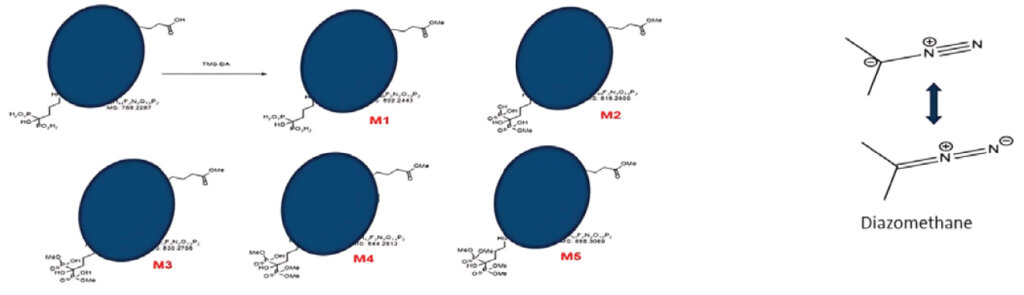
Figure below demonstrates the improvement in chromatographic behaviour and sensitivity by chromatograms of NCE with and without derivatization.
Case Study 2: Chemical Derivatization of Neurotransmitters using Dansyl Chloride
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that act as messengers, transmitting signals from one neuron to another or between nonneuronal body cells across chemical synapses. They facilitate the exchange of information throughout the brain and body. Dopamine, epinephrine, serotonin, and histamine are biomarkers associated with conditions such as insomnia, depression, epilepsy, schizophrenia, and other diseases. To evaluate efficacy of NCEs and to understand disease conditions, quantitative assessment of these biomarkers in response to treatment is of immense importance. Quantifying biomarkers and neurochemicals in complex biological matrices such as plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain tissue remains a challenging task due to the presence of contaminants and trace levels of analytes. These challenges often necessitate prior concentration or purification procedures before analysis.
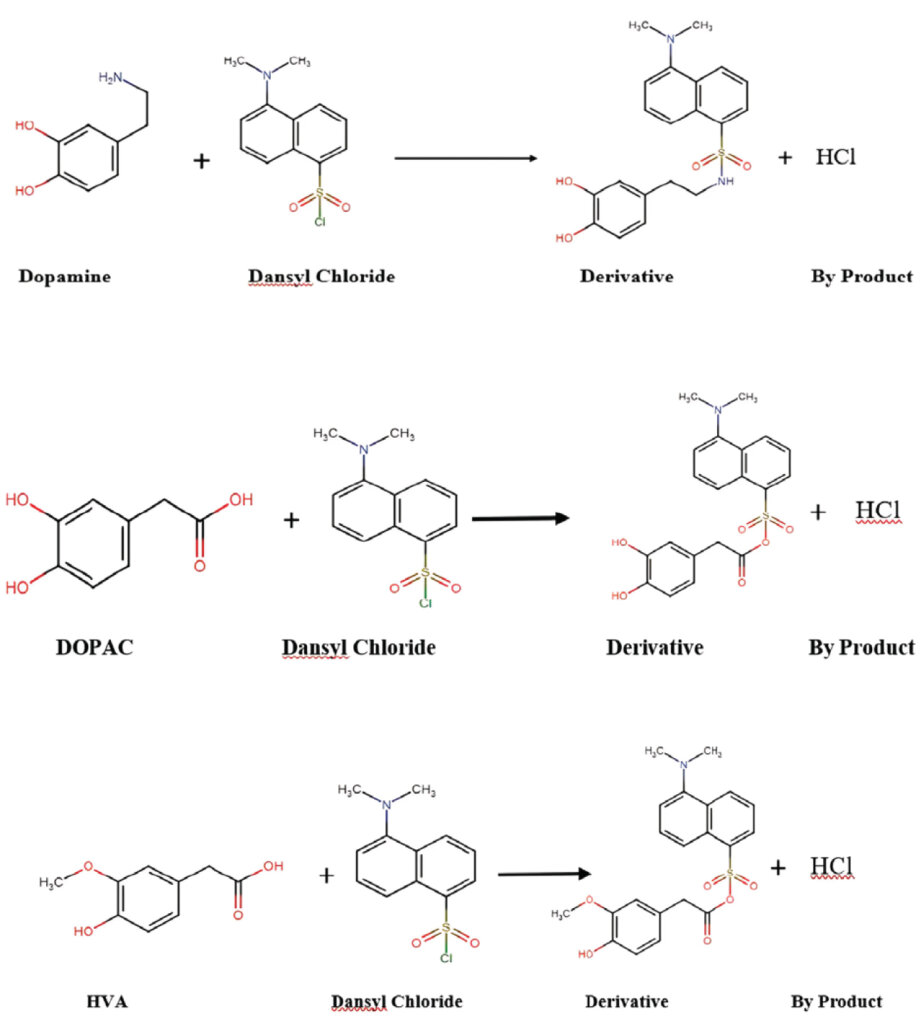
To quantify dopamine and its metabolites, the primary amines and hydroxyl groups in their chemical structures were targeted for derivatization with Dansyl chloride. Upon reaction with Dansyl chloride, dopamine forms a triple derivative, 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) forms a double derivative, and homovanillic acid (HVA) forms a single derivative product.
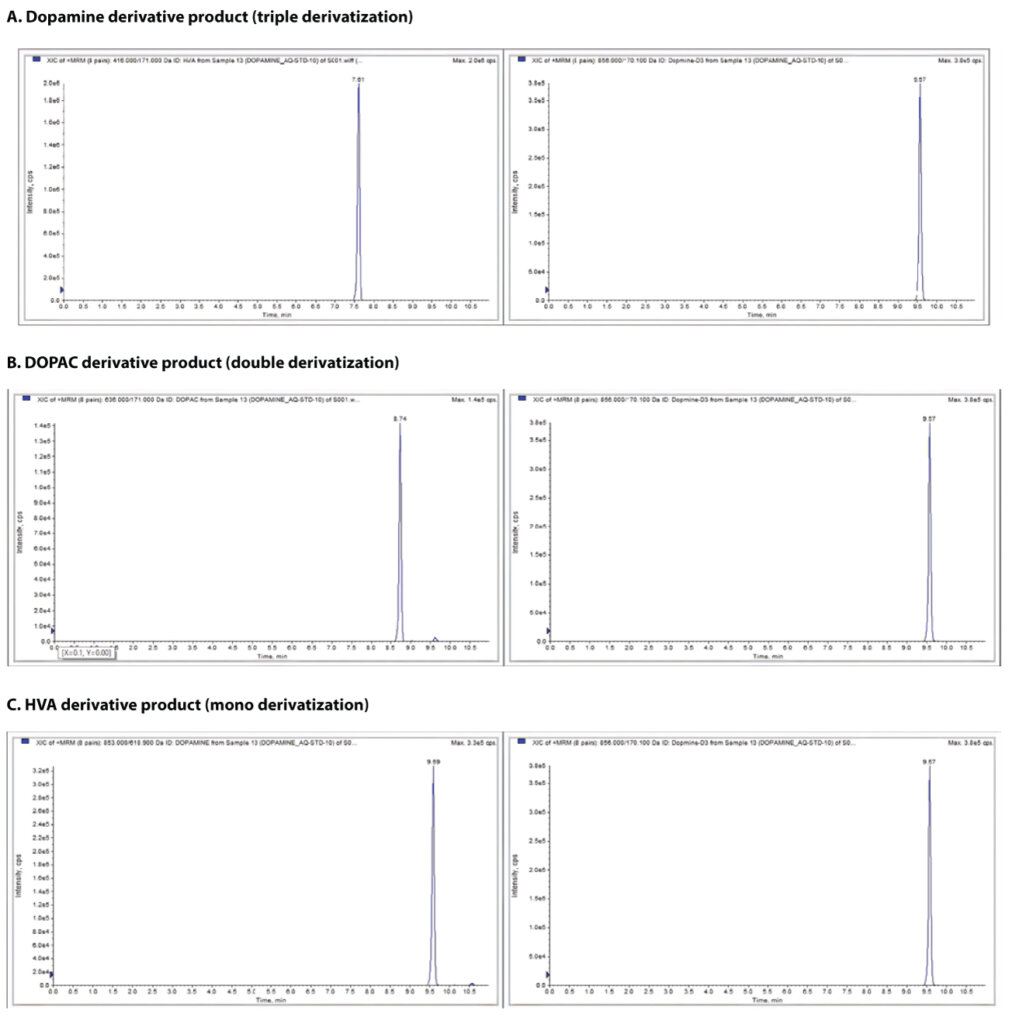
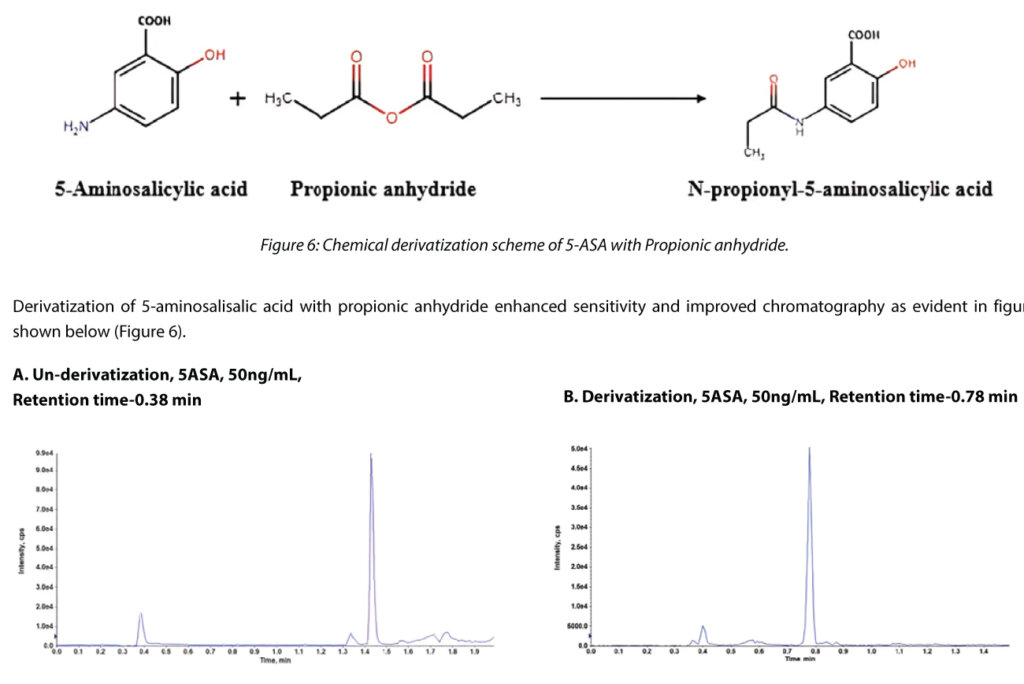
Case Study 3: Chemical Derivatization using Propanoic Anhydride
5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) is a metabolite of sulfasalazine, indicated in the treatment of active ulcerative colitis and for preventing relapses of the disease during remission. The quantification of 5-ASA is challenging due to its low molecular weight, and poor chromatographic retention and extraction from biomatrices. Therefore, the amino group was derivatized with propionic anhydride to enhance ionization efficiency and improve chromatographic retention on a conventional column. Chemical derivation involving propanoic anhydride was successfully used to improve chromatographic retention time and sensitivity of 5ASA in LC-MS/MS based method.
Syngene’s Expertise in Chemical Derivatization for LC-MS/MS Bioanalysis
LC-MS is widely recognized and accepted for its sensitivity and selectivity in detecting trace-level compounds. However, direct analysis of some molecules remains tricky due to lack of ionizable functional groups. Further complicating the analysis process are issues like molecules having rigid structures, resistance to fragmentation, poor retention on LC column etc. The chemical derivatizing method is often used to address these issues during DMPK bioanalysis.
Syngene has extensive experience in chemical derivatization technique both in terms of expertise and infrastructure to enable early and accurate detection of trace-level compounds. This in turn would prove useful in supporting bioanalytical studies for drug development.
References
- Christiana Mantzourani , Maroula G Kokotou. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Derivatization-Based Methods for the Determination of Fatty Acids in Biological Samples. Molecules 2022;27(17):5717 (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283012387_ Derivatization_methods_for_LC-MS_analysis_of_endogenous_compounds )
- Derivatization for liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry analysis of small-molecular weight compounds (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0165993619302948)
About the author








