In the dynamic landscape of drug discovery, accurate and sensitive quantification of biomarkers is imperative for understanding disease mechanisms and evaluating therapeutic efficacy. This blog details a successful bioanalytical program at Syngene, where the DMPK team developed a robust LC-MS-based quantitative method to measure biomarker 2-AG in mice brain tissues. The method offers valuable insights into the biomarker’s role in developing a drug that can be used to treat mood and anxiety disorders.
The role of 2-AG in affective disorders
2-AG, a crucial component of the endocannabinoid (eCB) system, has been identified as a potential biomarker in affective disorders such as anxiety and depression. Deficiency in 2-AG is thought to contribute to these conditions. Evidence suggests that normalizing 2-AG signaling could result in an effective therapeutic approach.
In a published study, stressed CD1 mice treated with the MAGL inhibitor JZL184 (10 mg/kg) administered as an intra-peritoneal injection demonstrated a two-fold increase in 2-AG concentration in brain tissue. Additionally, JZL184 was shown to reverse anxiety and depressive behaviors in specific mouse models, underscoring the therapeutic potential of targeting 2-AG pathways.
Bioanalytical method development: Quantifying 2-AG
Given the endogenous nature of 2-AG, the development of a reliable quantification method presented unique challenges. The strategy to develop a biomarker quantification method differs from conventional methods due to the presence of 2-AG in naïve samples. The liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method was fine-tuned for sensitivity and accuracy in detecting 2-AG in mouse brain tissue.
Major method development milestones were as follows:
- Verification of 2-AG peak involving verification of the molecular ion peak and fragmentation pattern of 2-AG between endogenous material and authentic standard
- Ensuring stringent control on temperature and pH to achieve desired sensitivity and result consistency, since the presence of albumin in serum promotes the rapid conversion of 2-AG to 1-AG
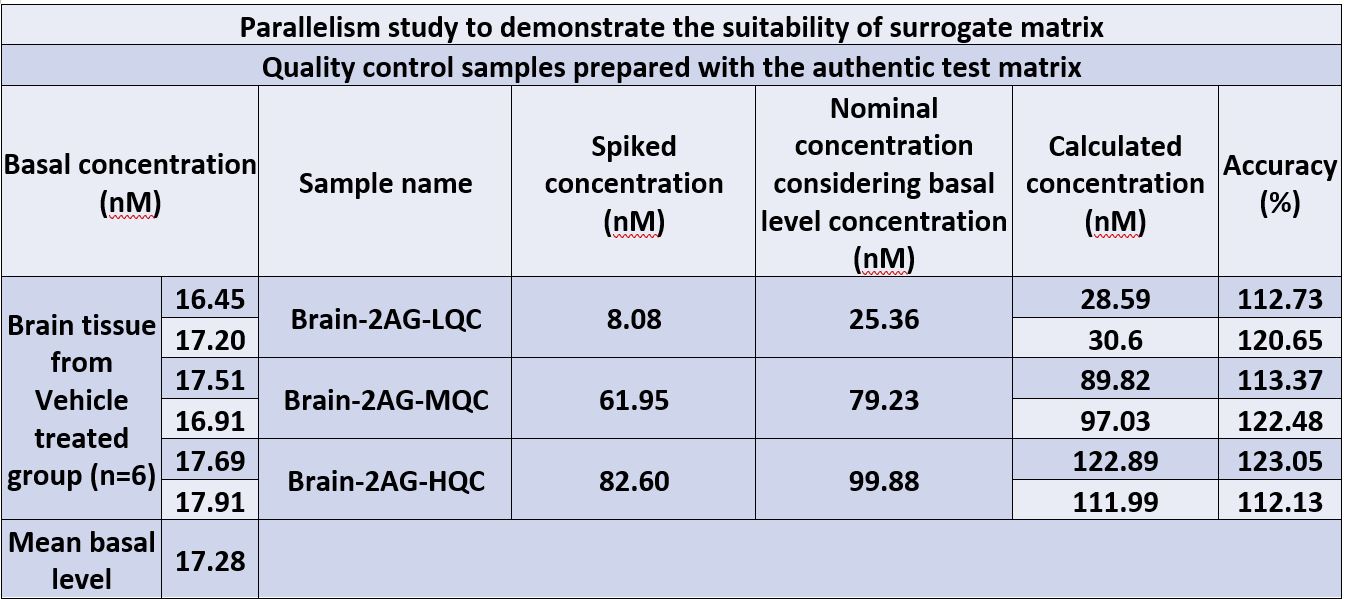
- Selection of appropriate surrogate matrix and parallelism study qualification
- Determining the basal level of 2-AG in untreated animals
- Confirmation of biomarker modulations demonstrated by the control group and comparing it with published data
Verifying 2-AG peak
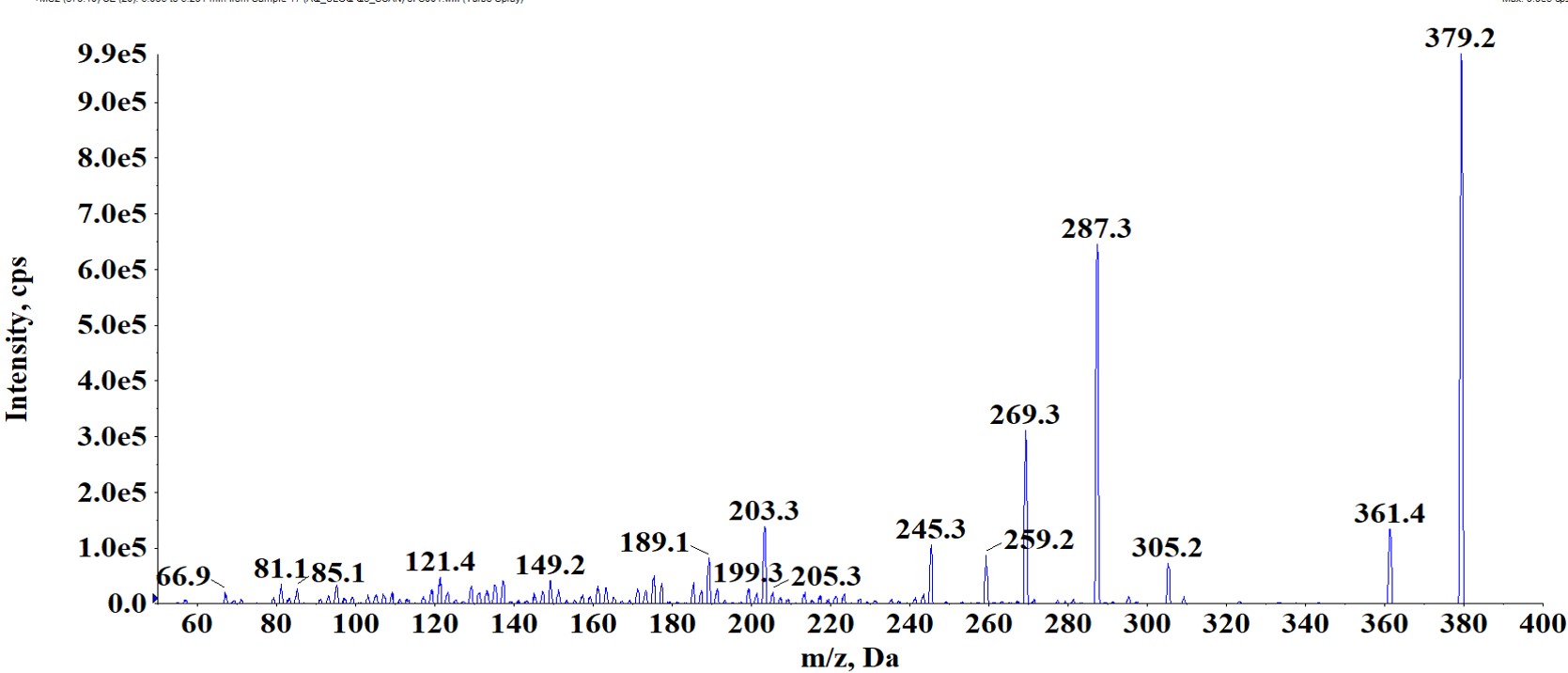
Unlike typical xenobiotics, biomarkers are endogenous. Hence, the routine strategy for optimization of MS parameters or peak detection cannot be followed.
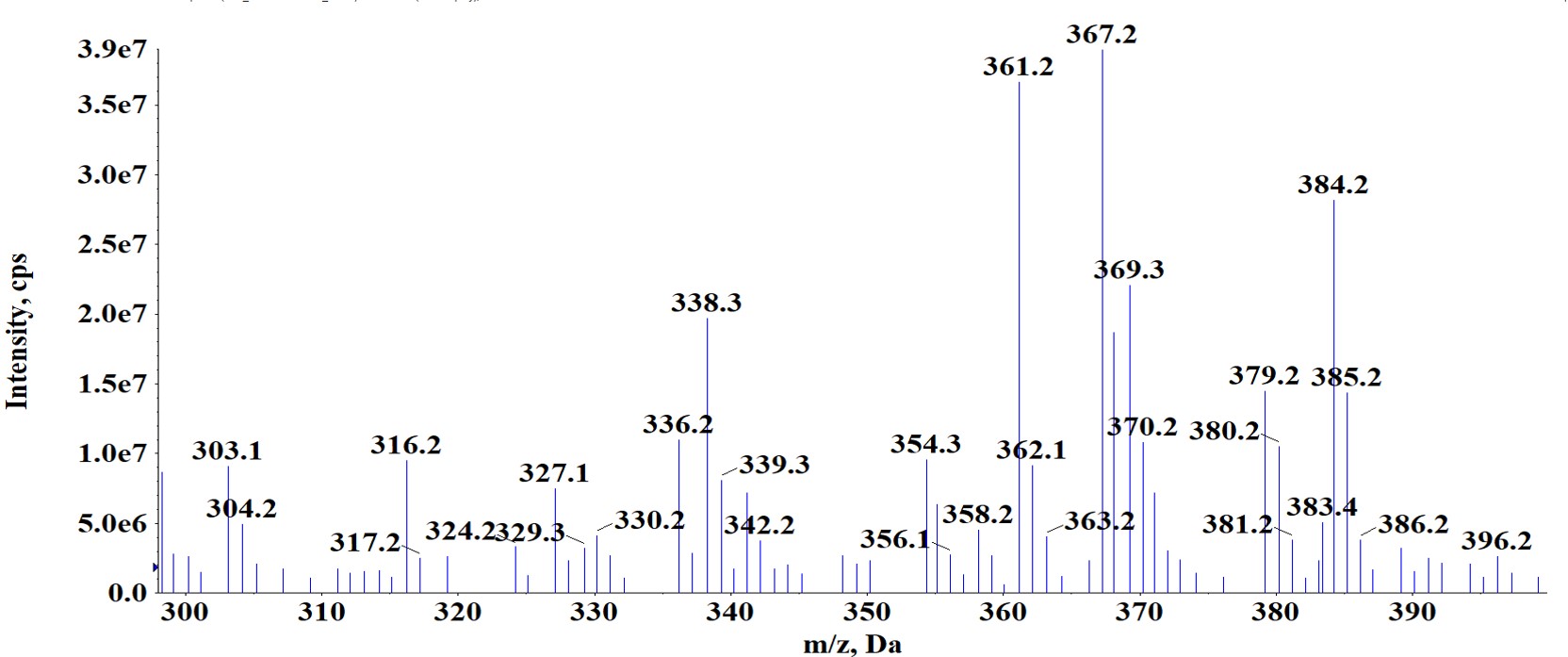
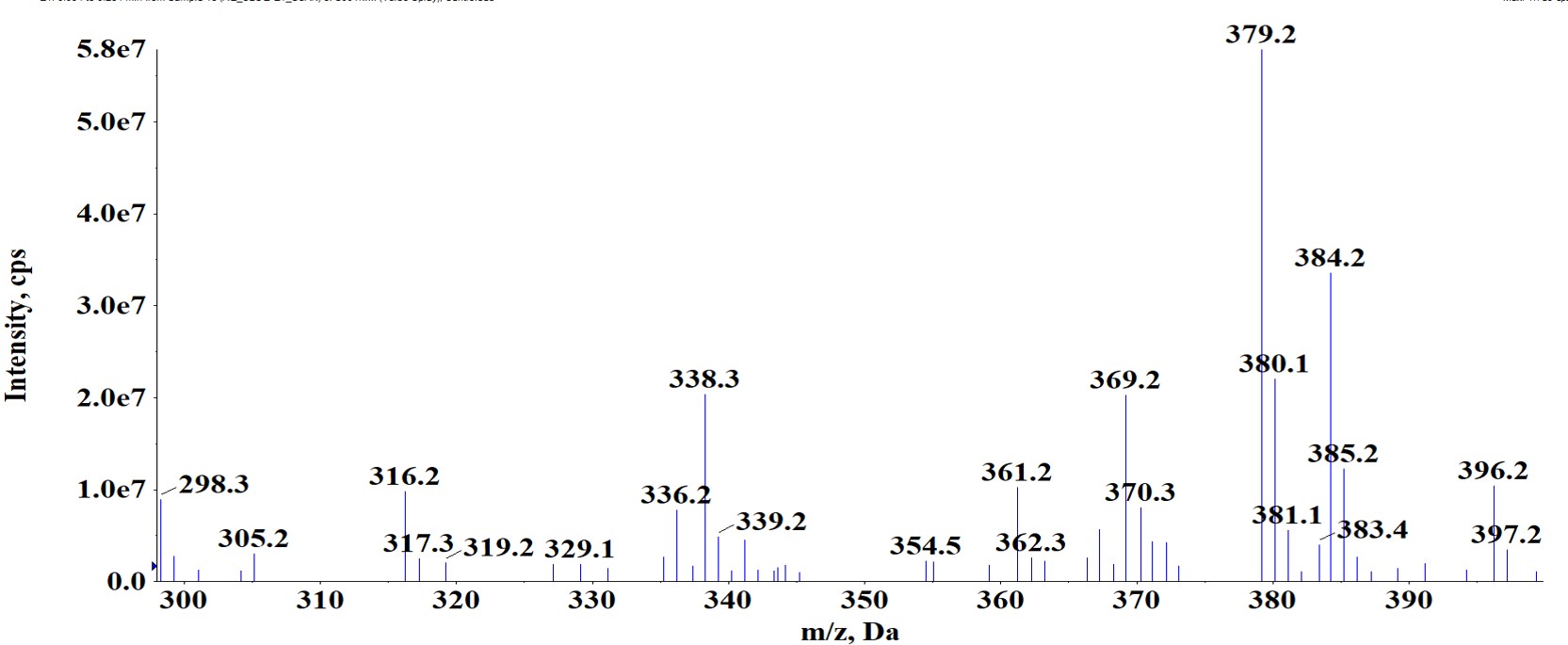
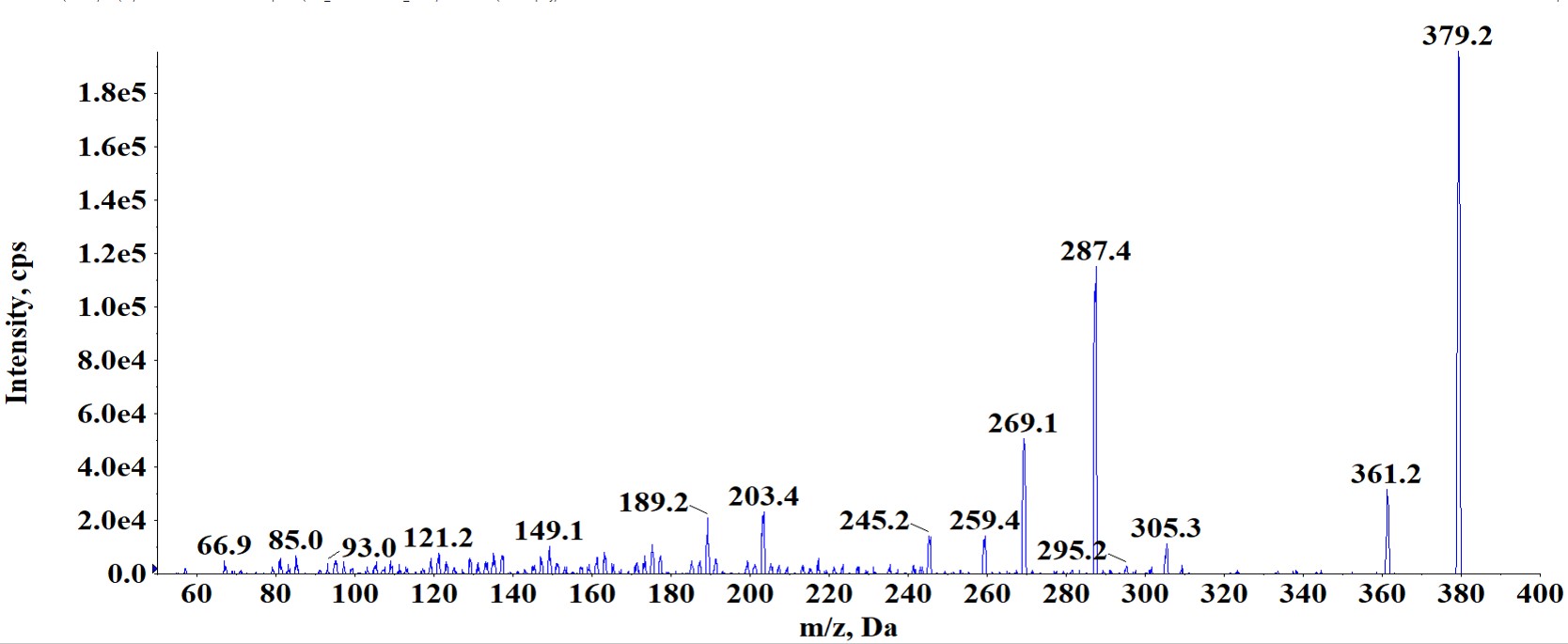
We performed verification of molecular ion and fragmentation pattern of 2-AG by comparing endogenous material with the authentic standard.
(A) Verification of molecular ion
(B) Verification of fragmentation pattern
The molecular ion and fragmentation pattern were found to be identical for both endogenous material and the authentic standard.
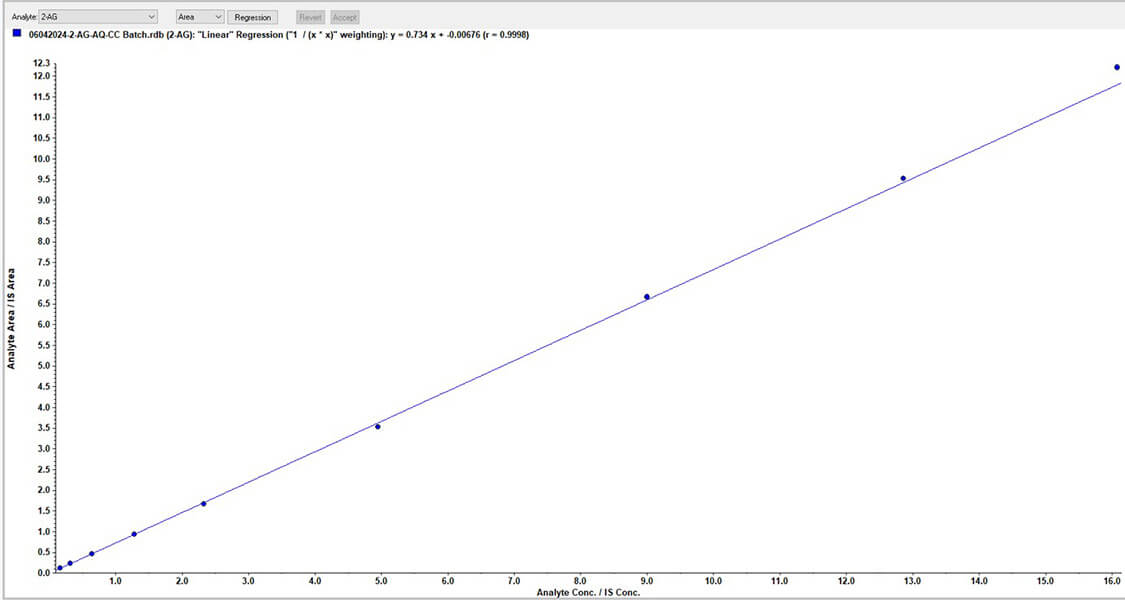
Since 2-AG is endogenous in nature, we prepared a calibration curve in acetonitrile to determine the 2AG concentrations in mouse brain samples.
Extraction methodology
Following the protein precipitation technique (ice-cold acetonitrile containing labeled internal standard was employed as the precipitation agent), we processed the mouse brain samples.
Determining endogenous levels
To determine the endogenous levels, we quantified the brain samples from a vehicle-treated group, n=6, against the calibration curve prepared with the surrogate matrix to determine basal levels. The mean endogenous level of 2AG in brain samples was found to be 17.28 nM.
LC-MS/MS operating parameters and method details
UHPLC | Shimadzu |
Mobile Phase | A: 0.1% formic acid in water B: 0.1 % formic acid in Acetonitrile |
Analytical column | Phenomenex kinetex C18 100*3.0mm,5μ |
Flow Rate | 0.8 mL/min |
Injection volume | 1μ L |
MS System | AB Sciex Triple Quard 5500 |
Ionization Source and Polarity | ESI , Positive MS/MS |
2AG (Q1/Q3) | m/z : 379.1/287.2 |
2AG-D5 | m/z: 384.2/287.2 |
Method qualification
Our team conducted a parallelism study with the test matrix to ensure the suitability of the surrogate matrix and method qualification. The method was found to be highly accurate and precise, with an accuracy percentage ranging between 112 and 123%.
Biomarker modulation and treatment impact
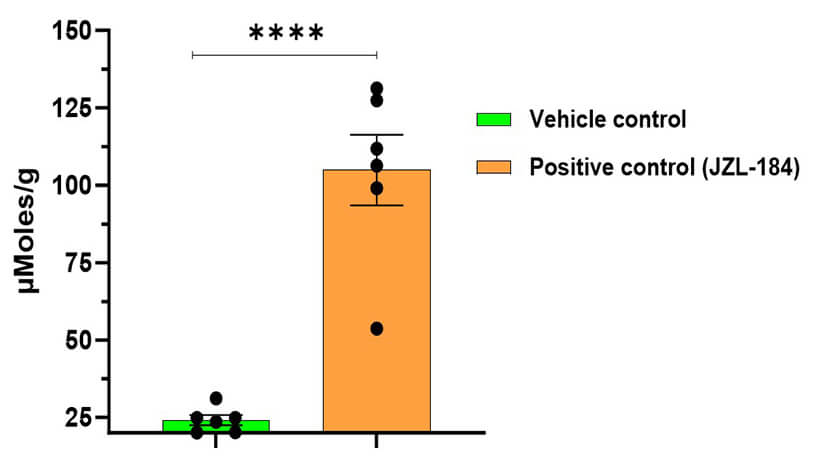
Our in-house study confirmed a nearly five-fold increase in 2-AG levels in the brain samples of mice treated with JZL184 compared to the vehicle-treated control group. This significant elevation in 2-AG highlights the inhibitor JZL184 effectiveness and provides valuable data supporting the therapeutic approach for targeting 2-AG in anxiety and depressive disorders.
Figure 7: Brain left hemisphere 2-AG levels (calculated concentration)
Conclusion: Fit-for-purpose bioanalytical method
The development of this fit-for-purpose bioanalytical method for 2-AG quantification is a critical step in advancing the understanding of the endocannabinoid system’s role in mood disorders. The method’s sensitivity and precision ensure reliable measurement of 2-AG levels in brain tissue, aligned with published data.
By leveraging Syngene’s advanced DMPK services, pharmaceutical companies can enhance their drug discovery efforts, especially in areas targeting the modulation of endogenous biomarkers like 2-AG.
Syngene specializes in developing customized bioanalytical solutions for both small molecules and biologics. Our bioanalytical methods are tailored to meet the unique challenges of early-stage drug discovery, providing robust, reliable data to drive decision-making in preclinical development.
To learn more, contact our experts