Pharmaceutical organizations worldwide are grappling with the escalating challenges posed by nitrosamine impurities in their products. The potential carcinogenicity of nitrosamines has raised concerns among regulatory authorities, prompting the need for robust solutions to ensure product safety, regulatory compliance, and overall industry reputation.
In recent years, several high-profile drugs have been recalled due to the detection of nitrosamine impurities. These incidents have further heightened awareness and regulatory scrutiny of these impurities.
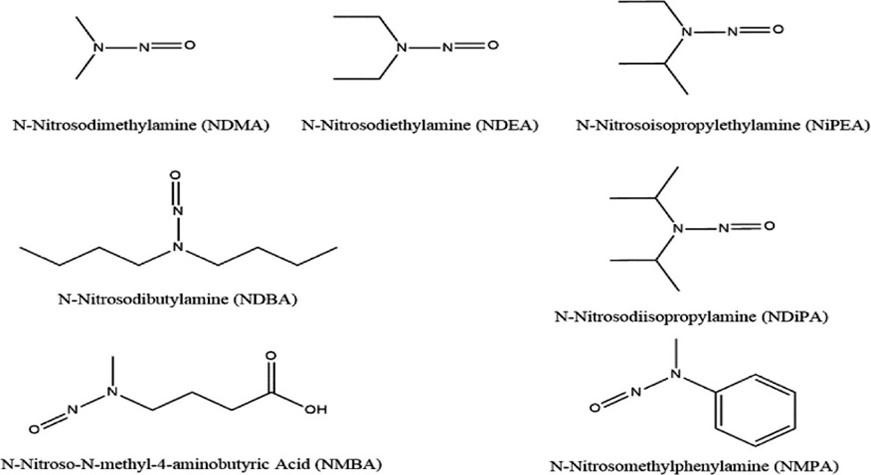
Figure 1: Structures of potential nitrosamine impurities in drug substances and drug products1
What are nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities
Nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities (NDSRIs) are nitrosamines that can form in drug substances or products under certain conditions. These include:
Chemical reactions: Nitrosamines can form through various chemical reactions, especially under acidic conditions. Commonly, they form from secondary and tertiary (first cleave into secondary amines) amines reacting with nitrosating agents like nitrites (and nitric oxide, sodium nitrite, dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrous acid).
Manufacturing processes: Certain manufacturing processes or conditions, such as the presence of nitrite contaminants or the use of amines and amides, can lead to the formation of nitrosamines.
Storage conditions: Degradation of drug substances or excipients over time, especially under specific storage conditions, can also result in the formation of nitrosamines.
Key challenges facing pharma companies on NDSRIs
Scrutiny and compliance pressures: Regulatory agencies globally are intensifying their focus on nitrosamine impurities, necessitating stringent compliance with evolving guidelines. Adherence to complex regulatory standards is becoming challenging, with potential consequences such as product recalls and market restrictions.
Complexity in detection and analysis: The intricate nature of nitrosamine impurities demands sophisticated analytical techniques for accurate detection and quantification. Many pharmaceutical organizations struggle with the implementation of these advanced methods in their existing workflows.
Supply chain vulnerabilities: Nitrosamines may originate from various sources within the supply chain, including raw materials and intermediates. Managing and mitigating these vulnerabilities requires thorough assessments and proactive measures, often straining existing quality control processes.
Time sensitivity and urgency: The dynamic nature of regulatory updates and the urgency to address nitrosamine concerns create a time-sensitive environment. Organizations need prompt solutions to comply with current regulations and to stay ahead of potential issues that may arise during inspections.
Syngene’s approach to NDSRI risk assessment
We have developed a strategic framework to identify at-risk active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) for NDSRIs. This framework aligns with recent guidance from the Health Authority and the World Health Organization (WHO) and addresses the industry’s need for clear-cut definitions.
Our nitrosamine formation framework is based on the following:
- Understanding the chemistry of the API: In the case of vulnerable APIs like secondary amines, nitrosamines can be formed by reaction with nitrosating agent under susceptible conditions like elevated temperature, acidic conditions, and liquid phase
- Assessing potential mutagenicity/ genotoxicity: Enhanced Ames Test, COMET assay
- Computational toxicology to determine acceptable limits (AI) for NDSRIs: Carcinogenic potency categorization approach (CPCA) reports from Derek Nexus (Lhasa, UK) including acceptable intake (AI) limits
Answering these questions helps determine if an API is susceptible to nitrosation, thereby streamlining compliance with regulatory guidelines.
Application of Syngene’s risk assessment framework
We have supported clients globally since nitrosamine became the topic of focus. As a first step, we engage in a detailed conversation with the customer to assess their API and current formulation, serving as a foundation for structuring our study. This is followed by a comprehensive approach to managing nitrosamine impurities.
- Equipment for analytical tests, including LC-MS/MS, HRMS, and GC-MS/MS systems
- Capability in highly sensitive and specific analytical techniques to detect nitrosamine impurities at the microgram level
- A highly qualified team to develop and implement analytical methods, including validation and stability
- State-of-the-art analytical labs equipped with advanced instrumentation in GMP Lab (Health Authority certified) for product release
- Expert toxicological support, including acceptable limits calculation using in-silico tools and genotoxicity testing (enhanced AMES test, COMET assay, etc.)
While regulatory bodies continue to refine expectations surrounding nitrosamine risk assessments, Syngene’s framework empowers researchers, reduces costs, and ensures patient safety.
Trust in pharmaceutical products is our priority. Our experienced team stands ready to address NDSRI-related challenges efficiently, providing informed and quantifiable solutions tailored to customer needs.
References
- Elsevier Vol 2, November 2022, 100037
- WHO good manufacturing practices (GMP) considerations for the prevention and control of nitrosamine contamination in pharmaceutical products, Working document QAS/24.943, April 2024
- Health Canada: Guidance on nitrosamine impurities in medications “Evaluating and managing the risks of N-nitrosamine impurities in human pharmaceutical, biological and radiopharmaceutical”
- Nitrosamine Impurities – Understanding Risks, Overcoming Challenges | Technology Networks